Overview
Stateful Dataflows (SDF) is the embodiment of versatility in data pipelines. A utility that helps developers build, troubleshoot, and run full-featured event-driven pipelines (dataflows). SDF sparks innovation among data engineers. By leveraging fluvio, SDF seemlessly integrates event streaming with stateful processing.
Built in Rust and powered by WebAssembly, SDF dataflows are small, fast, and incredibly versatile. They empower engineers to write custom logic snippets that compile to WebAssembly and inject them into the dataflow for in-line processing. This custom logic can perform various tasks, from data transformations and error correction to malicious payload detection and complex stateful processing.
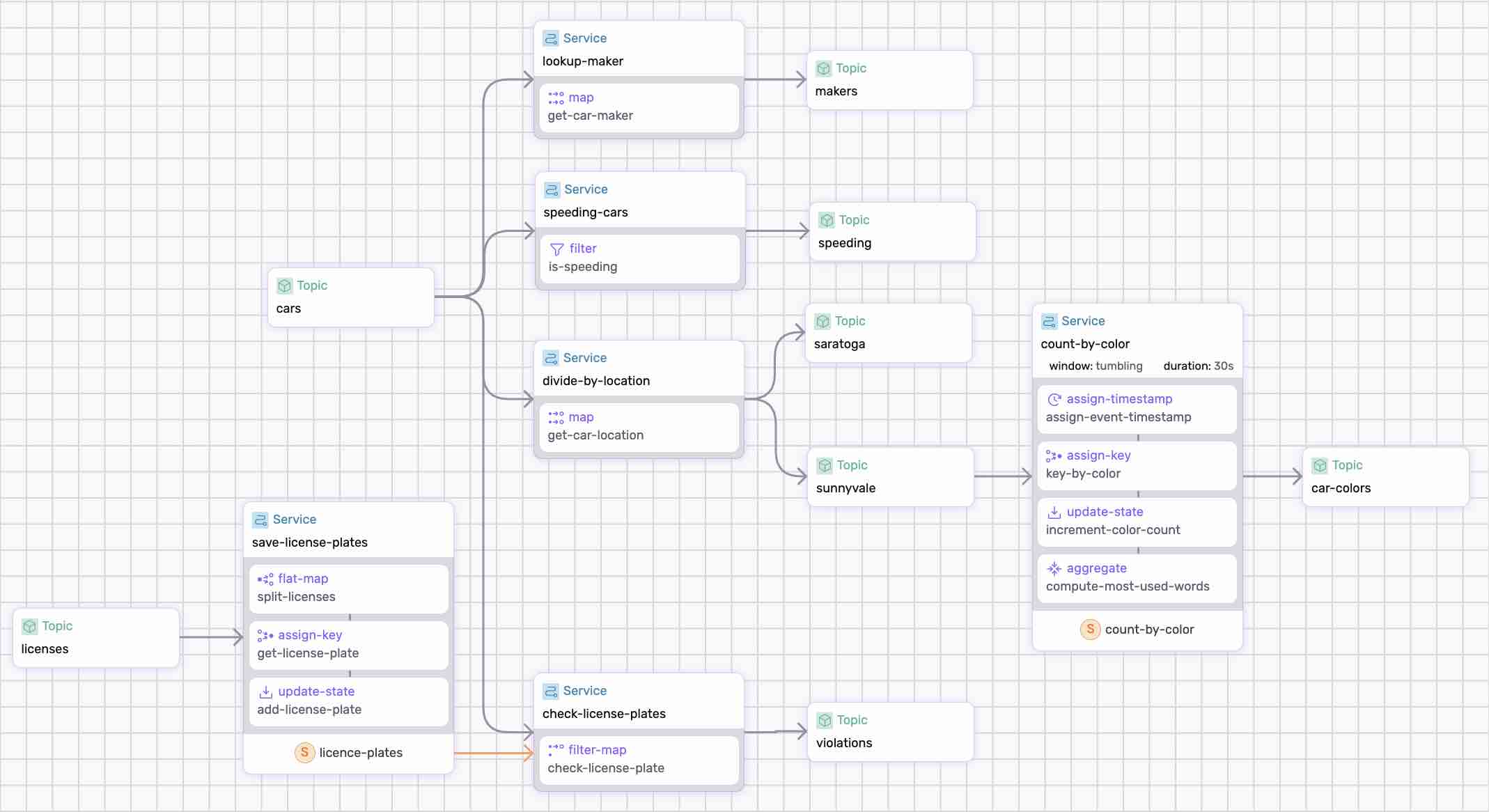
An example dataflow that performs various operations on data from traffic sensors. Try out the tutorial on github.
Stateful Dataflows vs. Big Data Stream Processing
Traditional Big Data processing frameworks like Kafka, Flink, KStream, and Spark force users to deploy and scale microservices externally from their streaming platform of choice. SDF introduces a more powerful paradigm by providing a solution for building fully-integrated yet scalable dataflows, streamlining the entire data processing workflow. Traditional frameworks are also built with Java, so any user-defined functions must be written in Java as well. Conversely, SDF empowers users to quickly develop and test individual services in their favorite programming language.
Stateful Dataflows vs. Legacy Solutions
Automating data operations within legacy technology stacks, spanning message brokers, databases, microservices, and batch jobs, typically demands months of setup and years of experimentation before yielding positive outcomes. Stateful Dataflows frees you from infrastructure intricacies and lets you focus on your core business logic instead.
Who is this for?
This platform is tailored for developers creating event-driven applications with continuous enrichment. The product streamlines the composition of dataflows with external sources such as databases, AI/ML models, and Redis caches, producing powerful results for analytics, applications, and operational dashboards.
How are Stateful Dataflows different from Fluvio?
Stateful Dataflows are an extension of Fluvio, leveraging the Fluvio infrastructure for communication and persistence. Fluvio is responsible for connectors, data streaming, and persistence, whereas dataflows handle data routing, transformations, and stateful processing.
How do I integrate this into my existing data architecture?
Fluvio connectors serve as the interface to external ingress and egress services. Fluvio publishes a growing library of connectors, such as HTTP, Kafka, NATs, SQL, S3, etc. Connectors are easy to build, test, deploy, and share with the community.
Next Step
In then Let's Get Started section, we'll walk through the steps to get started with Stateful Dataflows.